Coenzyme Q (ubiquinone or Q) is an organic lipophilic molecule essential for electron transport in the mitochondrial respiratory chain and works as an antioxidant. Primary coenzyme Q deficiency, a rare but severe pathology, has now been linked to mutations in 5 genes involved in the biosynthesis of human Q [1].
Knowledge of the eukaryotic Q biosynthetic pathway is largely due to the work done on yeast. The biosynthesis of Q takes place in mitochondria and requires at least nine proteins in yeast, all conserved in humans. Researchers from our laboratory, in collaboration with the EDyP team at the Large Scale Biology laboratory at our institute and the LAN at INAC have shown that the proteins Yah1p and Arh1p are essential for the first step of hydroxylation of Q biosynthesis in yeast
[2]. These researchers showed that depletion of Yah1p or Arh1p leads to the accumulation of a biosynthetic intermediate of Q. The characterization of this intermediate has enabled researchers at the Chemistry and Biology of Metals Laboratory to propose a new
in vivo precursor in yeast Q: para-aminobenzoic acid (pABA) (Figure). The pABA resembles to the well-known precursor of Q, the para-hydroxybenzoic acid, but differs from the latter by the substitution of a hydroxyl group with an amino group. We must therefore consider the existence of an additional step of deamination / hydroxylation in the biosynthesis of pABA when Q is used as a precursor.
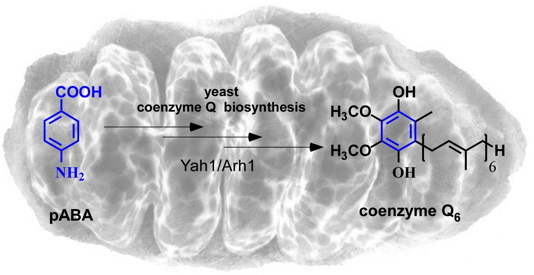
Coenzyme Q (ubiquinone or Q) is a lipophilic organic molecule composed of a substituted benzoquinone and of a polyprenyl chain. Coenzyme Q is represented here in a mitochondrion.
It should now be checked whether these new players of Q metabolism in yeast play a role in the biosynthesis of Q in mammals [3].